What are the timers and its registers?
- As their name suggests, the main purpose of a timer is to measure time and count external events.
- The 8051 microcontrollers have 2 timer/counters called T0 and T1.
- Timers can be used for generating clock pulses used for serial communication i.e. Baudrate.
Some Timer registers are
- Load registers
- TMOD registers
- TCON registers
1. Load registers
- Load registers are used to load timer counts.
- These registers are of 16 bit.
- The lower bit registers are called TL0/TL1.
- The higher bit registers are called TH0/TH1.
- TH0/TL0 is called timer 0.
- TH1/TL1 is called timer 1.
2. TMOD (Timer mode) register
- Both timer 0 and timer 1 use the same register called TMOD (Timer mode) to set the various timer operation modes.
- TMOD is an 8-bit register.
- The lower 4 bit for timer 0 and upper 4 bit for timer 1.
- The upper 2 bits i.e. Gate and C/T are used to specify the operation.
- The lower 2 bits i.e. M0 and M1 are used to set timer modes.
Different modes of timer
Mode M1 M2 Operation
0 0 0 13 bits
1 0 1 16 bits
2 1 0 8 bits
3 1 1 split
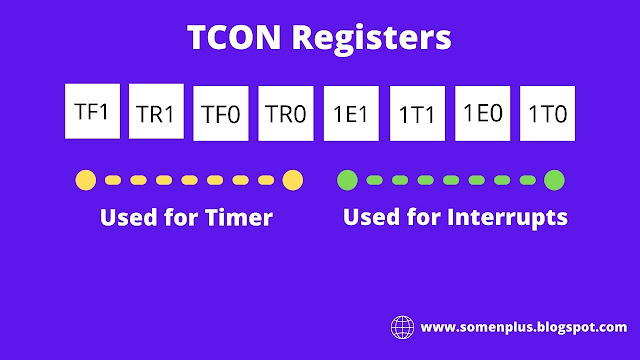
3. TCON ( Timer control ) register
- The upper 4 bits are used to store the TF and TR bits of both timer 0 and timer 1.
- The lower 4 bits are used for controlling the interrupt bits.
For Timer 1
- TF1 = 1 (flag bit is 1 i.e. counting is completed)
- TF1 = 0 (flag bit is zero)
- TR1 = 1 (start counting in timer 1)
- TR1 = 0 (stop counting in timer 1)
For Timer 0
- TF0 = 1 (flag bit is 1 i.e. counting completed)
- TF0 = 0 (flag bit is 0)
- TR0 = 1 (start counting in Timer 0)
- TR0 = 0 (stop counting in Timer 0)